Do banks need gamification?
In an era where traditional banking methods fall short of tech-savvy consumer expectations, gamification emerges as a game-changer.
From attracting new users through engaging challenges, rewards, and achievements to increasing retention with fun, game-like experiences, gamification is transforming the way banks connect with their customers.
-
Marina Mouka
- August 20, 2024
- 8 minutes

In the ever-evolving landscape of digital banking, customer engagement and retention have become more crucial than ever. Traditional banking methods no longer suffice to meet the expectations of tech-savvy consumers.
Enter gamification—a strategy that utilises game-like elements to transform everyday banking tasks into engaging and rewarding experiences. By incorporating features such as points, badges, leaderboards, and challenges, banks can now enhance engagement, improve retention, and add unique features to their services, creating a more interactive and enjoyable user experience.
This article delves into the necessity of gamification for banks, exploring its key principles, benefits, and challenges. We will also examine real-world examples and case studies to illustrate the impact of gamification in the banking sector. Finally, we will look ahead to the future trends poised to shape the industry.
As we navigate through these insights, it becomes evident that gamification is not merely a buzzword but a crucial tool for modern financial institutions.
What is gamification?
Gamification is the application of game-like mechanics in non-game contexts to make processes more engaging and enjoyable. In the realm of banking, this involves integrating elements such as points, badges, leaderboards, challenges, and rewards into web and mobile banking platforms. The goal is to transform routine financial tasks into interactive experiences that motivate users to engage more deeply with the app.
The effectiveness of gamification lies in its psychological underpinnings. For instance, the release of dopamine when completing tasks and earning rewards creates a sense of pleasure, encouraging continued use. Additionally, the concept of loss aversion—where users are motivated to avoid losing progress—can be leveraged through features like progress bars. These bars visually represent how close users are to achieving their financial goals, such as saving for a vacation.
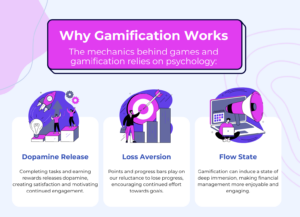
Another key aspect is the induction of a flow state, where users become deeply immersed in an activity, making it more enjoyable and focusing their attention. By incorporating these psychological triggers, gamification can significantly enhance user engagement and satisfaction.
Gamification stats and facts worth knowing about
The impact of gamification in banking is supported by compelling statistics and facts. A 2021 study by Zaguan University analysed data from 208 users of the Mint app, a personal financial management tool, to explore how gamification influences user engagement.
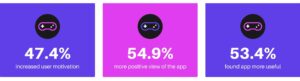
The findings were striking: gamification increased user motivation by 47.4%, with 62.2% of users planning to continue using the app due to its game-like features. Additionally, 54.9% of users reported a more positive view of the app, and 53.4% found it more useful.
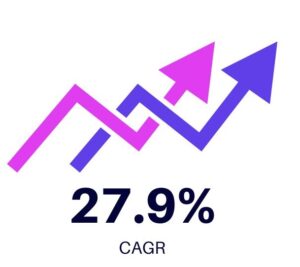 These numbers are not isolated. The global gamification market was valued at USD 10 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow to USD 116.68 billion by 2032, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 27.9%.
These numbers are not isolated. The global gamification market was valued at USD 10 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow to USD 116.68 billion by 2032, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 27.9%.
As affirmed by BBVA Open Innovation Report, some of the world’s largest banks and financial institutions have already adopted gamification, generating a value of $12.25 billion in 2021. 
North America leads this trend, with a market value of USD 3.8 billion in 2022, driven largely by the retail industry’s adoption of gamification.
Moreover, gamification has proven effective in enhancing financial literacy. For example, educational quizzes and challenges within banking apps help users understand complex financial concepts, leading to better financial habits.
Key principles and features of gamification
Gamification in banking is built on several key principles and features designed to enhance user engagement and satisfaction. These principles leverage psychological triggers to make financial tasks more interactive and enjoyable.

Benefits of gamification in banking
Gamification offers numerous benefits for banks and their customers. One of the most significant advantages is increased customer engagement. By incorporating game-like elements, banks can make routine financial tasks more interesting, encouraging users to spend more time on their apps. This heightened engagement often translates into improved customer retention, as users are more likely to continue using an app that they find enjoyable and rewarding.
Another key benefit is enhanced financial literacy. Gamified educational quizzes, challenges, and simulations help users understand complex financial concepts such as budgeting, saving, and investing. This not only empowers customers to make better financial decisions but also positions the bank as a reliable source of financial information, creating opportunities for upselling premium features and services.
Gamification also aids in promoting new services. Reward-based gamification can be an effective way to encourage users to try out new features, thereby increasing the adoption rate of these services. Additionally, gamification provides valuable data on user behaviour and preferences. By analysing how users interact with game elements, banks can gain insights into their customers’ financial goals and needs, allowing for better-tailored products and services.

Challenges of gamification
Despite its benefits, gamification in banking comes with its own set of challenges. One of the primary concerns is maintaining the seriousness of financial management. While gamification aims to make banking more engaging, it is crucial to strike a balance so that the core functionalities and the professional nature of banking are not compromised.
Another challenge is catering to a diverse audience. Digital banking solutions are used by people of various demographics, each with different goals, interests, and levels of financial literacy. Designing gamified experiences that appeal to such a broad audience can be complex and resource-intensive.
Lastly, gamification is not a one-time implementation but an ongoing process. Banks need to continuously update and improve their gamification strategies to keep users engaged over the long term. This requires a commitment to regular updates, new challenges, and evolving game mechanics to meet the changing needs and preferences of users.
5 Unique examples of gamification in banking

-
Standard Chartered’s 2021 Twist & Win
Standard Chartered Bank’s 2021 Twist & Win campaign used gamification to offer surprise cashback for credit card transactions. Integrated into the bank’s mobile app, the campaign featured personalised onboarding and a fun gumball machine animation for real-time cashback rewards. The gamification of the app aimed to encourage customers to use their credit cards. This strategy was successful as it boosted customer engagement and spending during the promotion.
-
Monobank’s mascot and badge reward system
Monobank, a Ukrainian banking app, has successfully integrated gamification to enhance user engagement. Users can earn achievements for various in-app activities, such as completing their profile information. This system of badges and rewards motivates users to interact more frequently with the app, fostering a sense of accomplishment and loyalty.
Another unique aspect of the Monobank app is its signature cat mascot. This mascot differentiates the app from competitors, making it memorable and special. Moreover, studies have shown that mascots help build brand trust and customer rapport.
-
Progress bars for the win for Starling Bank and Qapital
Starling Bank and Qapital have taken a unique approach by incorporating progress bars to help customers visualise their savings goals. For instance, Qapital’s Shared Goals feature allows users to share their saving goals with others, adding a social element that can motivate users to reach their targets faster. This visual representation of progress plays on the psychological principle of loss aversion, encouraging users to continue saving and motivating them to reach their goals faster.
-
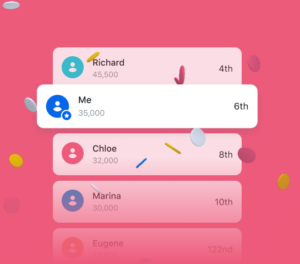
Revolut’s lotteries and leaderboards
When expanding in Europe, Revolut launched a university competition, urging students to boost their school’s ranking by signing up. Targeting a younger crowd, the leaderboard highlighted communities, not individuals. This gamification strategy targeted our need for belonging. Shared goals can create a strong sense of community, making them a powerful motivator. The result? Over 100 universities and thousands of students joined in.
Revolut has also employed gamification through weekly lotteries. Users can collect points, which serve as entries into these lotteries, and see how they rank against others. This competitive element not only makes the app more engaging but also incentivises them to perform more transactions, thereby increasing app usage.

-
Monzo’s savings challenge
One of the UK’s earliest app-based challenger banks, Monzo, is well-known for its gamified banking experience. With features like a task-based onboarding menu and achievement challenges, Monzo has grown its user base to over 5 million without physical branches.
A standout example is Monzo’s 2022 ‘run and save’ scheme. By linking Monzo accounts to Strava or Fitbit, the bank’s users could transfer money to their savings ‘pots’ when they met their running goals. These pots could be locked or restricted, making it harder for users to access funds and helping them stay committed to their savings goals.
The future of gamification in banking
The future of gamification in banking is set to be shaped by three key trends: integration with AI, cloud-based gamification solutions, and the development of mega financial platforms. AI-driven gamification will enable banks to offer personalised experiences by analysing user behaviour and preferences, thereby enhancing engagement and satisfaction. Cloud-based solutions will provide scalability and flexibility, making it easier for banks to implement and update gamification features without significant upfront costs.
Moreover, the rise of mega financial platforms, where financial services are integrated with technology on a large scale, will further drive the adoption of gamification. These platforms will offer a seamless, engaging user experience, combining various financial services under one roof.
As these trends converge, gamification is set to become an omnipresent feature in the banking industry, transforming how users interact with their financial institutions and making banking more engaging and enjoyable.

 Bobsguide is a
Bobsguide is a